In the above equation, g is gravity, 32.2 ft/s. Given an initial angular displacement and zero initial velocity, the above equations can be solved to obtain the angular displacement and velocity of the pendulum. The 2nd order DE has to be split up into two first order ones in order to obtain a solution.
The variable-step method of Dormand & Prince was applied to solve the above IVP. The results for a 170 deg initial displacement are shown below.

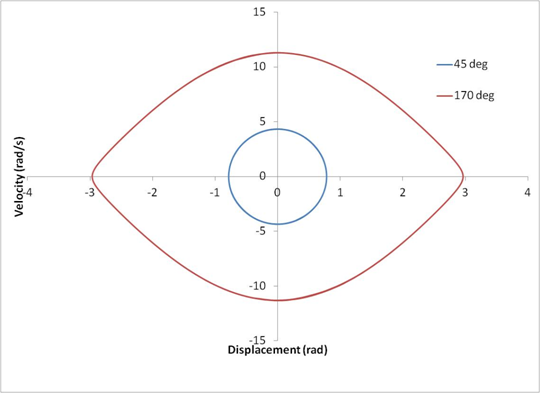
A comparison of the velocity vs displacement for 45 deg and 170 deg initial values is shown below.
No comments:
Post a Comment