Orbit equations refer to a class of ODE’s in Astronomy that describes the motion of planets due to the gravitational forces that each body exerts on the others. The two-body orbit equations are represented by the following differential equations (ref: Enright & Pryce, Two Fortran Packages for Assessing Initial Value problems, ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, Vol. 3, No. 1, pp 1-27, 1987):
The initial values are defined by
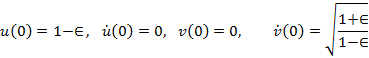
The variable step
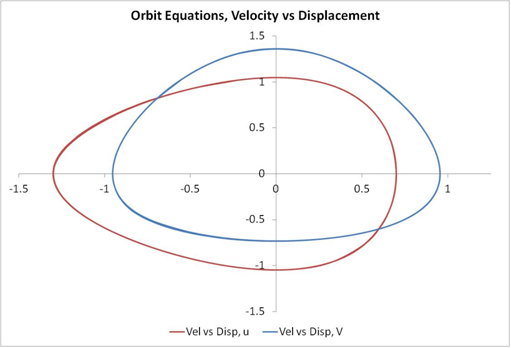
Verner’s method was employed to solve the two-body problem using an epsilon of 0.3 for the initial values. The solutions of velocity versus displacement for u and v are shown below:
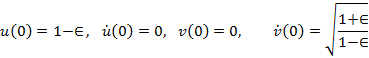

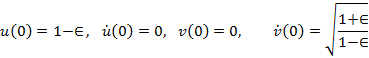

No comments:
Post a Comment