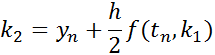
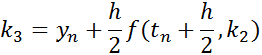
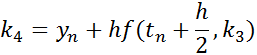
Using k1-k4 from the above, the next step is calculated as:
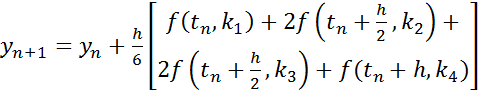
The algorithm for the RK4 method can be summarized as:
1) % Define step size (h), initial function y(0), initial time t0, final time tf
2) nosteps = (tf – t0)/h
3) for i ← 1 to nosteps
- Calculate derivative function f[t0,y[i-1]]
- k1 ← f[t0,y[i-1]]
- Calculate f[t0,k1]
- k2 ← y[i-1] + 0.5*h*f[t0,k1]
- t0i ← t0 + 0.5*h
- Calculate f[t0,k2]
- k3 ← y[i-1] + 0.5*h*f[t0i,k2]
- k4 ← y[i-1] + h*f[t0i,k3]
- y[i] ← y[i-1] + (h/6)*{f[t0,k1] + 2 f[t0i,k2] + 2 f[t0i,k3] + f[t0+h,k4]
- t0 ← t0 + h
- k1 ← f[t0,y[i-1]]
- Calculate f[t0,k1]
- k2 ← y[i-1] + 0.5*h*f[t0,k1]
- t0i ← t0 + 0.5*h
- Calculate f[t0,k2]
- k3 ← y[i-1] + 0.5*h*f[t0i,k2]
- k4 ← y[i-1] + h*f[t0i,k3]
- y[i] ← y[i-1] + (h/6)*{f[t0,k1] + 2 f[t0i,k2] + 2 f[t0i,k3] + f[t0+h,k4]
- t0 ← t0 + h
4) Display results
[…] RK4 method was used to solve these equations with a step-size of 0.001, and the results for y1 and y2 are […]
ReplyDelete